We have all heard the term “social engineering” before. What exactly is it, though? Social engineering is a technique used by threat actors to manipulate individuals to perform actions that can violate the security of information or disclose confidential data. Instead of attempting to exploit technical aspects, it focuses on cybersecurity’s biggest weakness: humans.
How Does Social Engineering Exploit Humans?
Social engineering takes heavy advantage of human psychology to exploit people. By targeting traits such as fear, curiosity, urgency, and trust, attackers can manipulate individuals into performing undesirable actions. When trying to accomplish a task, attackers will craft situations that will pressure people into making a decision without properly thinking it through. Technology has allowed this technique to flourish now due to the anonymity and broad reach of targets, due to the internet. It is essential to properly train all users in an organization on how to recognize and prevent social engineering attempts.
How Do Attackers Use These Traits To Their Advantage?
As mentioned above, common traits attackers will use include fear, curiosity, urgency, and trust. These traits are often enough to get people engaged and to act without properly verifying the claim. Here are some ways that attackers may use these traits to target behaviors:
Fear: An attacker will attempt to scare you into performing an action that is not safe. A common technique that a user may see is a message claiming, “Your system is infected with malware. Click here now to prevent data loss.”
Urgency: Attackers will attempt to make people take immediate action by imposing an unrealistic deadline for a task or an urgent action. Common emails that will try to use urgency may claim, “Your password is expiring today. Click here to change it now.”
Trust: Attackers may also attempt to connect with a target to build a mutual ground before conducting an attack. This could include claiming to have mutual friends, connections, or experiences to appear legitimate.
Common Social Engineering Attacks
With all this talk about social engineering, you are probably wondering what it includes. Here are some of the most common types of attacks that we are prone to encountering:
Phishing
Phishing is one of the most common types of social engineering. Attackers will attempt to pose as a legitimate source to provide sensitive information. Phishing is not a “one size fits all” and can present itself in multiple ways.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Smishing uses text messages (SMS) to target users. These messages typically include “Failed delivery” attempts or messages claiming account breaches.
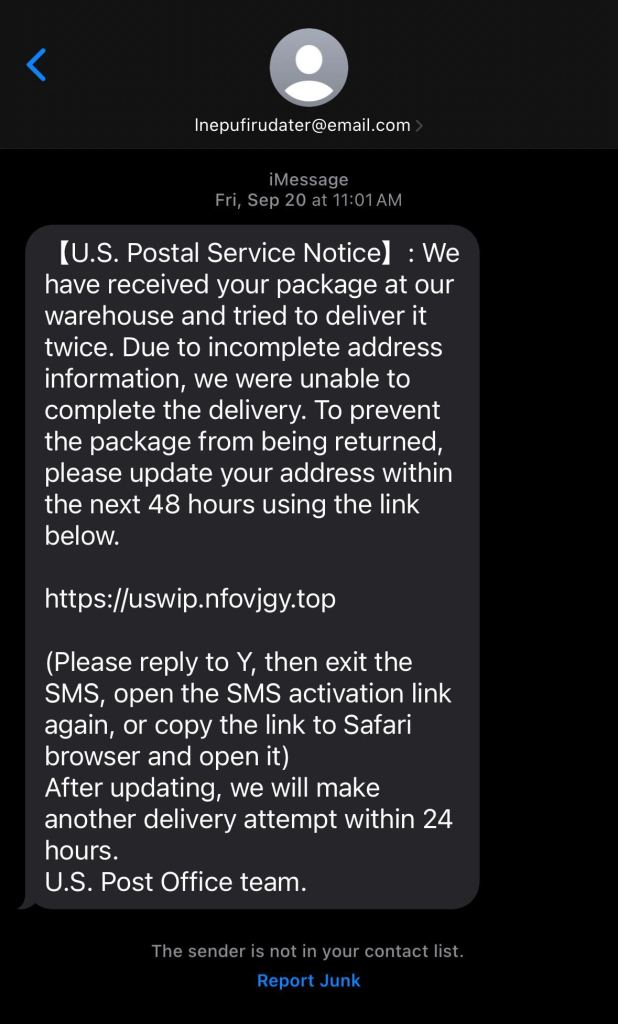
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Vishing uses phone calls to manipulate people into providing information. These calls often come from seemingly legitimate numbers and use professional scripts.
- Spear Phishing: Using well-crafted emails, attackers will attempt to trick individuals into clicking on links and provide sensitive information, including credentials or banking information, or download malware. These emails target a specific group or person to increase the likelihood of success.
- Whaling: Targets high-level executives or other organizational VIPs to request sensitive data, financial information, or payments.
Pretexting
An attacker will attempt to create a fictional scenario to justify their request for access to systems or sensitive information. Common scenarios you may see include:
- A vendor requesting a contract verification
- An employee requesting urgent access to a system
- An executive requesting information for a confidential task
Impersonation
Impersonation includes both physical and digital methods. Physical impersonation techniques can involve someone claiming to be a maintenance or delivery worker to gain access to a building or secure area through tailgating. Attackers may also wear fake ID badges or uniforms to look legitimate and act confident to avoid suspicion. Digital impersonation may require a more keen eye to notice, as it can involve creating clones of legitimate websites (i.e., http://www.google.com vs http://www.g0ogle.com) to steal information, or creating an email address similar to a legitimate one (i.e., user@company.org vs user@componey.org). It is always important to verify that people are who they say they are and validate that information is correct.
Baiting
Attackers will attempt to leave physical devices in well-populated areas, hoping someone will take and use them. The most popular form of baiting is USB drives that will be left in high-traffic areas that contain malware. When these drives are connected, they can run malware that will steal files, launch a ransomware attack, or even monitor your device long-term to steal credentials through keyloggers.
How Can You Keep Yourself Safe From Social Engineering?
Falling for a social engineering attempt can lead to devastating consequences. Here are some ways that you can identify and prevent social engineering attacks:
- Be wary of unsolicited calls, emails, or text messages. Always verify the sender’s identity if you aren’t sure if a message is legitimate.
- Do not share personally identifiable information (PII) or financial information with individuals you do not know.
- Never click on suspicious links. Contact your IT team for assistance if you are unsure if a link is legitimate.
- Install and maintain anti-virus software on your machine to monitor for any malicious files or software.
- Always utilize multifactor authentication on your accounts.
Conclusion
Social engineering attacks continue to show that they are dangerous and will always pose a threat. As cybersecurity professionals always say: “humans are the weakest link.” Continuous training and awareness are essential for preventing social engineering attacks. Staying alert and aware can be the difference between falling victim to an attacker and successfully recognizing a social engineering attempt.

Leave a comment